LTE video tutorial
LTE physical layer
LTE link layer design
Introduction to LTE architecture
This
article
provides an overview of the LTE radio interface,
together with a more in-depth description of its features such as
spectrum flexibility,
multi-antenna transmission, and inter-cell
interference control. The performance of LTE and some of its key
features is illustrated with simulation results.
This article provides a high-level overview of LTE and some of its key components: spectrum flexibility, multi-antenna transmission, and ICIC. Numerical simulations are used to show the performance of the first release of LTE, as well as assess the benefit of the key features. Indeed these contribute strongly to LTE meeting its performance targets. An outlook of the evolution of LTE toward LTE-Advanced and full IMT-Advanced capabilities complete the article. Clearly, LTE offers highly competitive performance and provides a good foundation for further evolution.
This article provides a high-level overview of LTE and some of its key components: spectrum flexibility, multi-antenna transmission, and ICIC. Numerical simulations are used to show the performance of the first release of LTE, as well as assess the benefit of the key features. Indeed these contribute strongly to LTE meeting its performance targets. An outlook of the evolution of LTE toward LTE-Advanced and full IMT-Advanced capabilities complete the article. Clearly, LTE offers highly competitive performance and provides a good foundation for further evolution.
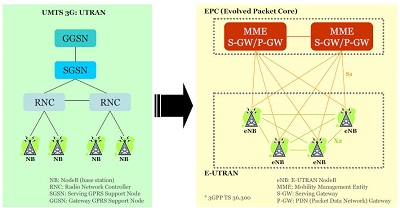
LTE network architecture
EPS architecture overview
This excellent video by Russell DeLong covers the EPS in detail. The topics covered here are:
Terminology clarifications for "4G LTE" and the EPS.
Overview of each component of EPS. Russell walks you through the role of the MME, the S-GW and the P-GW.
Overview of each logical connection between each component on the EPS.
Terminology clarifications for "4G LTE" and the EPS.
Overview of each component of EPS. Russell walks you through the role of the MME, the S-GW and the P-GW.
Overview of each logical connection between each component on the EPS.
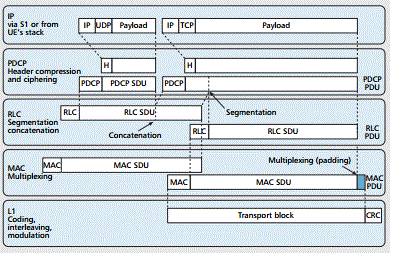
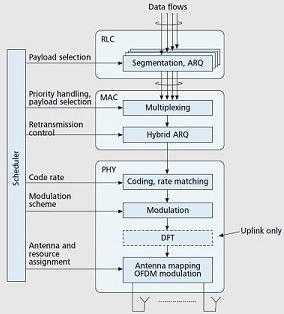
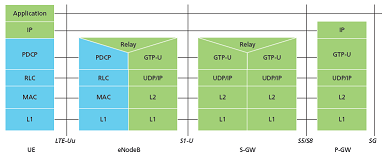
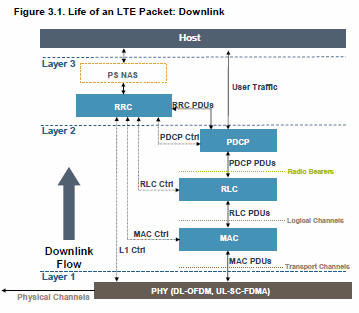
LTE channels and protocol layers
This paper provides an overview of the MAC for 3GPP™ Long Term Evolution (LTE) also referred to as E-UTRAN, with
a focus on the handset or User Equipment (UE). The protocol stack functions consist of the Medium Access Control
(MAC), Radio Link Control (RLC), Packet Data Convergence Protocol (PDCP), and Radio Resource Control (RRC).
LTE uses all the time on the downlink for conveying data; the downlink PHY is fully scheduled so there are no gaps due to arbitration or contention except for the initial access on the random access procedure. The downlink carries multiple logical channels over one link, so a lot of information is multiplexed together in one transport block, as opposed to other networks where any given packet is only carrying one type of information at a given time, such as in a control plane or a user plane..
LTE uses all the time on the downlink for conveying data; the downlink PHY is fully scheduled so there are no gaps due to arbitration or contention except for the initial access on the random access procedure. The downlink carries multiple logical channels over one link, so a lot of information is multiplexed together in one transport block, as opposed to other networks where any given packet is only carrying one type of information at a given time, such as in a control plane or a user plane..
Very useful..
ReplyDelete